Hip & Elbow testing & Health in Doodles & Poodles
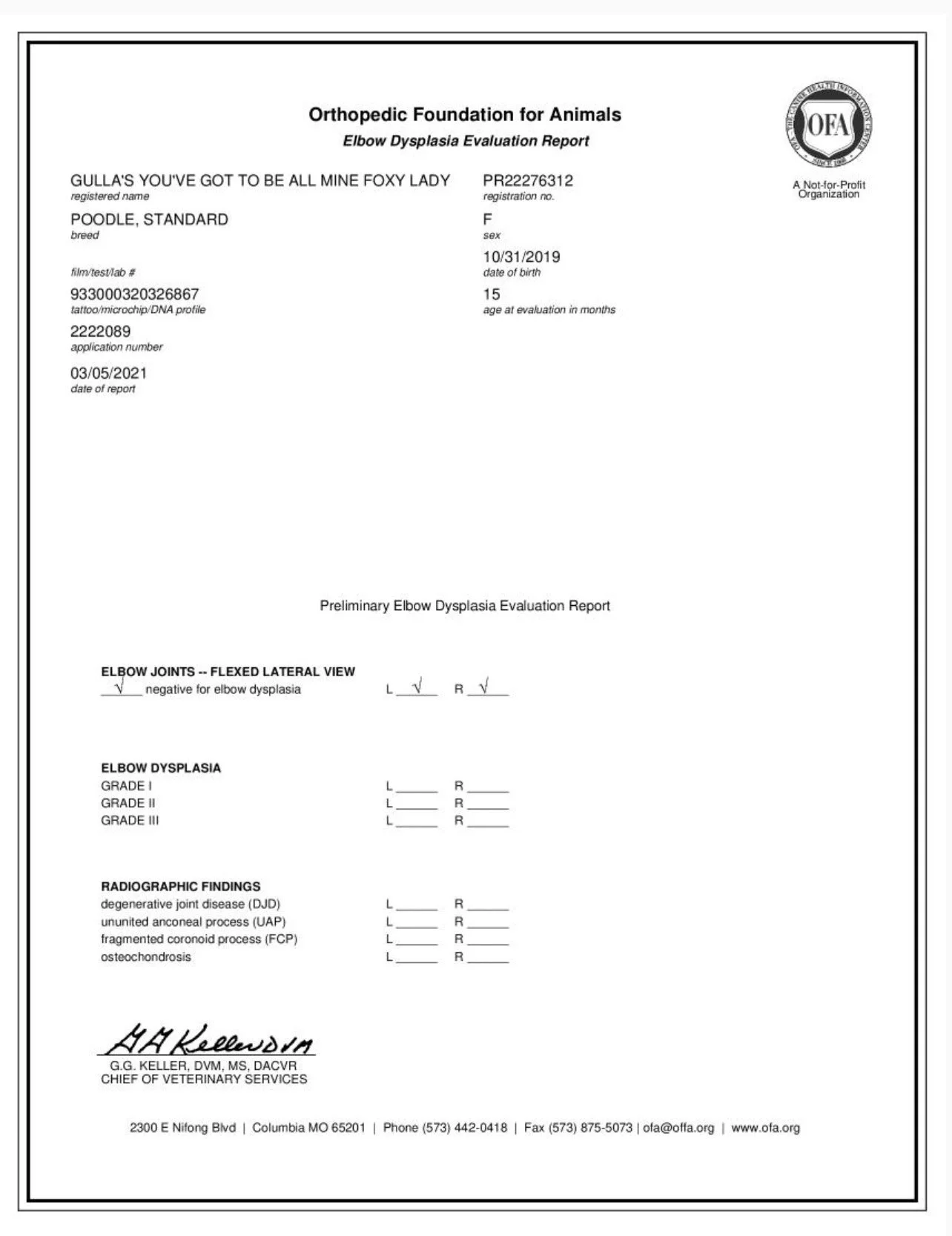
Sample OFA of FOXY
OFA stands for the Orthopedic Foundation for Animals, which is a non-profit organization that evaluates and maintains records of hip and elbow dysplasia in dogs. Dogs can be evaluated for hip and elbow dysplasia through x-ray, and if they pass the OFA evaluation, they will be given a certification number and their results will be recorded on the OFA website. This information can be used by breeders to make informed decisions about breeding and can help to reduce the incidence of these inherited conditions in future generations of dogs.
Hip and elbow dysplasia are inherited conditions that affect the development of the hip and elbow joints in dogs. Hip dysplasia occurs when the hip joint does not develop properly, which can lead to pain, arthritis, and difficulty moving. Elbow dysplasia is a group of inherited conditions that affect the elbow joint, which can also cause pain and difficulty moving. Both conditions are more common in certain breeds of dogs, such as larger breeds like German Shepherds and Labrador Retrievers. Symptoms can include limping, stiffness, and difficulty rising or climbing stairs. Treatment options include weight management, exercise modification, physical therapy, and medication, but in severe cases, surgery may be needed.
The PENN Hip (University of Pennsylvania Hip Improvement Program) is another method used to evaluate hip dysplasia in dogs. It is similar to the OFA evaluation in that it uses x-rays to assess the hip joint and assigns a score to the dog based on the degree of hip dysplasia present. The PENN Hip method is considered to be more accurate than the OFA method as it evaluates the joint space of the hip, which is an indicator of arthritis, rather than just the congruency of the joint. Some breeders prefer to use the PENN Hip method in addition to or instead of the OFA evaluation to get a more comprehensive assessment of their breeding stock's hip health.
Hip health is important for dogs to maintain a good quality of life and to prevent pain and mobility issues. Good hip health can be maintained through a combination of proper nutrition, exercise, and weight management.
A diet that is balanced and appropriate for the dog's size, breed, and activity level can help to maintain a healthy weight and support joint health. A moderate exercise regimen that includes a combination of low-impact activities, such as walking and swimming, and muscle-building exercises can help to strengthen the muscles around the hip joint and improve mobility.
Nutrition plays an important role in maintaining joint health in dogs. A diet that is balanced and appropriate for the dog's size, breed, and activity level can help to support joint health and reduce the risk of conditions such as hip dysplasia and osteoarthritis.
One important nutrient for joint health is glucosamine and chondroitin, which are naturally occurring compounds that are important for the health and repair of cartilage. These supplements can help to reduce inflammation and improve joint mobility. Omega-3 fatty acids, such as those found in fish oil, also have anti-inflammatory properties and can help to support joint health.
Other important nutrients for joint health include vitamin C, which is essential for the formation of collagen, and vitamin D, which helps the body to absorb calcium. Minerals such as calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium are also important for maintaining strong bones and joints. Glucosamine and chondroitin are naturally occurring compounds that are important for the health and repair of cartilage in the joints. They can be found in some foods, but most commonly are available in the form of supplements.
Foods that are rich in glucosamine include:
Shellfish, such as crab, lobster, and shrimp
Bones, particularly those from chicken, turkey, and pork
Organ meats, such as liver and kidney
Foods that are rich in chondroitin include:
Cartilage and tendons from animals, such as chicken feet and beef trachea
Bone broth
In addition to the right nutrients, it's also important to maintain a healthy weight for the dog, as excess weight can put added strain on the joints.
It's important to note that certain breeds of dogs are more prone to hip dysplasia and other hip-related issues, so it's important for owners of these breeds to be especially vigilant about maintaining their dogs' hip health. If a dog is showing signs of hip pain or mobility issues, it's important to consult with a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
To schedule an OFA evaluation for hip and elbow dysplasia in dogs, you will need to find a veterinarian who is certified to perform the evaluation. The Orthopedic Foundation for Animals (OFA) maintains a list of certified veterinarians on their website, which you can search by location to find a veterinarian near you.
Once you have found a certified veterinarian, you will need to schedule an appointment for the evaluation. You should inform the veterinarian that you would like to have your dog evaluated for hip and elbow dysplasia and provide them with the necessary information, such as your dog's breed, age, and any relevant medical history.
The OFA evaluation typically involves taking x-rays of the dog's hips and elbows, which will be sent to the OFA for evaluation. The OFA will then assign a score to the dog based on the degree of hip and elbow dysplasia present and issue a certification number if the dog passes the evaluation. The results will be recorded on the OFA website, which can be accessed by the public.
It's important to note that the dog should be at least two years old, and not older than three years, before getting OFA evaluation, as the bones are not fully developed before that age, and after three years the dog may have arthritis, which can skew the results.
Preventive measures such as early screening and genetic testing can also be helpful to maintain hip health in dogs.
The Orthopedic Foundation for Animals (OFA) maintains a list of certified veterinarians on its website, which you can search by location to find a veterinarian near you. You can go to their website, https://www.ofa.org, and select the state "Wisconsin" to find OFA-certified veterinarians in Wisconsin.
You can also contact the Wisconsin Veterinary Medical Association (WVMA) for a list of OFA-certified veterinarians in the state. They maintain a list of board-certified specialists, including those who are certified to perform OFA evaluations for hip and elbow dysplasia in dogs. Their website is https://www.wvma.org/ and you can contact them by phone (608) 257-3665.
You can also check with your local veterinary clinics, some of them may have OFA-certified veterinarians on staff or can refer you to one nearby.
It's important to schedule an appointment well in advance as OFA evaluations may require special equipment, and the veterinarian may need to schedule an additional appointment for the x-rays.